GNU Radio - Embedded Python Block
GNU Radio is a open source and free software which provides signal processing blocks to implement software radio. This is a very good software which can do both software simulation and even connect to external hardware. However, I found that the documentation of some of the blocks is not upto the mark (no offense to the developers). One such block is the Embedded Python Block. This is one of the most powerful blocks present in the software as it allows you to do custom calculations. However some very minute details are missing from the official wiki. I had made a doc with details of getting started with this block for one of the graduate level lab at IIT Bombay. In this blog post I’ll be sharing the same.
Embedded Python Block
GNU Radio provides an Embedded python block to do custom processing of the signals. This block is available under the name of “Python Block”.

By default, this block performs scaling of the signal. To revise the python code for this block follow the following steps:
- Double click on the block OR right click and choose properties
- Select “Open in Editor”
- Note: This will open an prompt asking editor to select. Select editor of your choice
- This will open a python script with the contents shown in the figure below
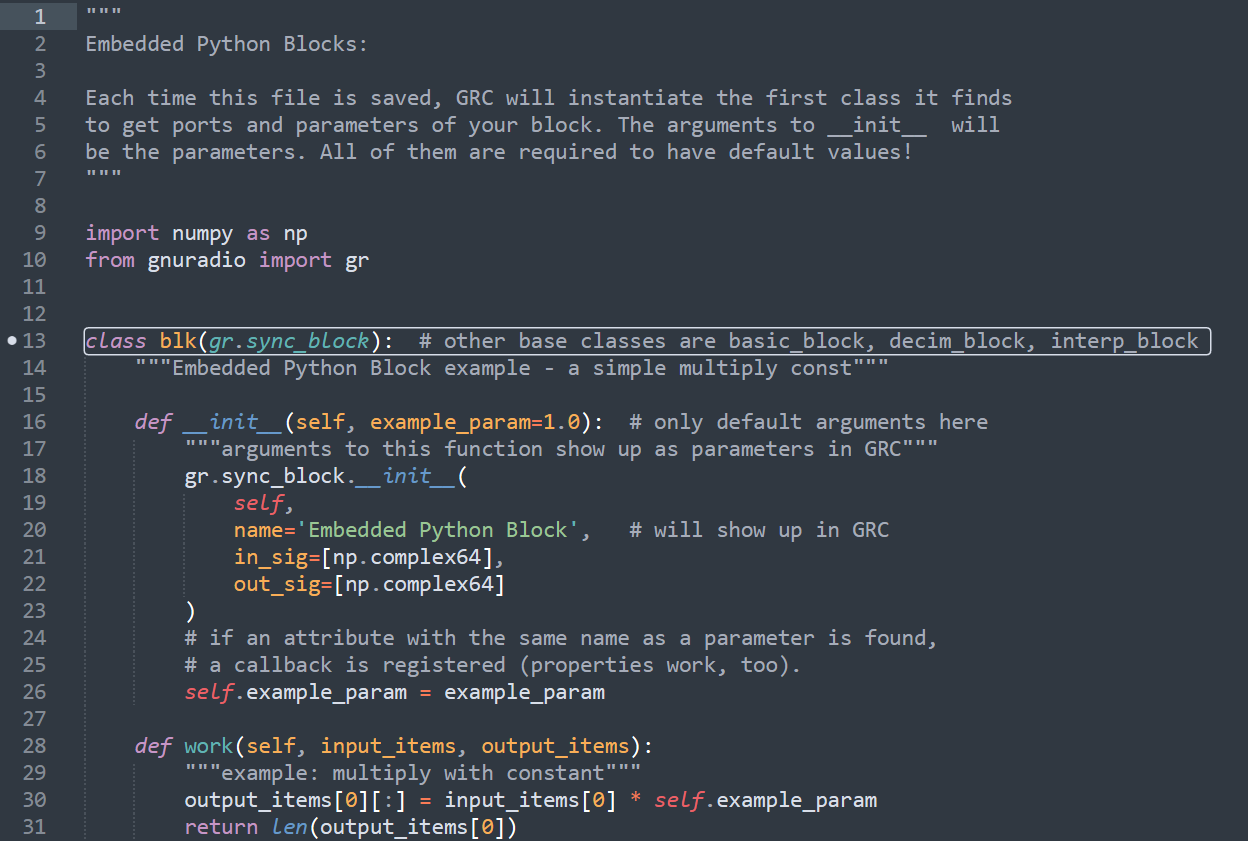
- There are 2 functions which you should edit: __init__ and work of the blk class. Note that this is class is a child of gnuradio’s sync_block class which will provide some of the functionalities.
__init__ function
- name="Embedded Python Block" is the name that will appear in the GNU radio’s GUI. You can change this name as per your wish
- in_sig=[np.complex64] defined the input type to the block. You can change this to one of the following type: np.int16 which is basically short data type, np.int32 which is int data type, np.float32 or np.float64 which are float data type and np.complex64. To add these parameters you can simply change the line as follows:
in_sig = [np.complex64, np.float32, np.int16]
This will add 3 inputs with the specified input data type

- out_sig=[np.complex64] works the same was as in_sig but with the output ports
- Adding Parameters: To add the parameters to the block, simply add them to the input arguments of the __init__ function. Make sure to add them as class variables if necessary
- Apart from the above points you can use the __init__ function as a per your wish following the rules of python programming language
work function
This is the function where code for processing the inputs and outputs would be written. This function have 2 arguments which should not be changed:
input_items & output_items
input_items is a list of numpy array of input signals. The inputs will be arranged as they are defined in the in_sig in init function. You can use various numpy functions and their it’s vectorization to your make your code run fast. Output_items follow the same logic with outputs.
For e.g. below is a simple code which scales the input and clips it’s amplitude
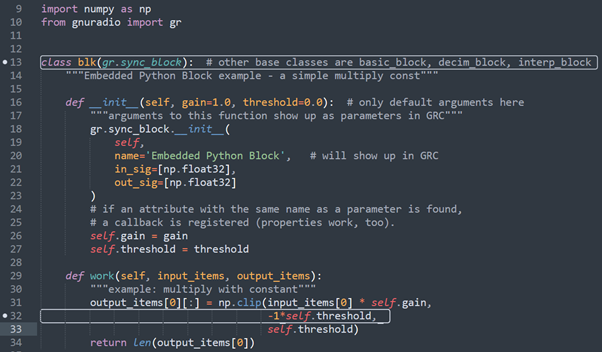
The work function returns as output an integer indicating the number of items in the list output_items. By default it returns len(output_items) which is the max length of output items(8192 by default). This means every call to the work function processes a block of input of len(output items) at a time.
Debugging Embedded Python Block
This is a very tricky task. I could not find log files of GNU radio. It does not show the error in the GUI. If there is an error in your EPB block code, the GNU radio will still create the flow-graph but the output of the EPB block will be taken as a zero vector. To avoid this, the only way I can suggest for debugging for now is to write a separate standalone script for checking the functionalities of your work function.